
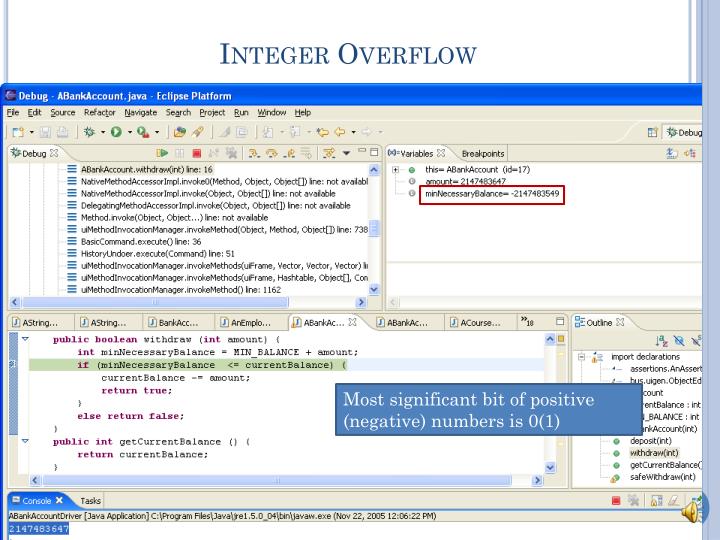
Key Terms circular nature Connecting the negative and positive ends of the domain of an integer family data type. It might take a while (thus it might appear to be in an infinite loop) for it to reach the negative 2 billion-plus value, before finally decrementing to positive 2147483647 which would, incidentally, stop the loop execution.
#Integer overflow code#
The above code accidentally decrements and the value of x goes in a negative way towards -2147483648 (the largest negative value in a normal four-byte signed integer data type). Let’s give an example of the loop executing for what appears to be for infinity (the third item on our list). Usually, the direction of counting (increment or decrement) need to be switched.
#Integer overflow update#

If a programmer sets up a counting loop incorrectly, usually one of three things happen: The use of the modulus operator in integer division is tied to the concepts used in modular arithmetic. Time-keeping on a clock gives an example of modular arithmetic.” (Modular arithmetic from Wikipedia)
Since the hour number starts over when it reaches 12, this is arithmetic modulo 12. Likewise, if the clock starts at 12:00 (noon) and 21 hours elapse, then the time will be 9:00 the next day, rather than 33:00. Regular addition would suggest that the later time should be 7 + 8 = 15, but this is not the answer because clock time “wraps around” every 12 hours there is no “15 o’clock”. If the time is 7:00 now, then 8 hours later it will be 3:00. …Ī familiar use of modular arithmetic is its use in the 12-hour clock the arithmetic of time-keeping in which the day is divided into two 12 hour periods. “In mathematics, modular arithmetic (sometimes called clock arithmetic) is a system of arithmetic for integers where numbers “wrap around” after they reach a certain value - the modulus. In theory, it should work for the Boolean data type as well but in most programming languages it does not for various technical reasons. This circular nature of the integer family works for both integer and character data types. This can be shown by using a normal math line, limiting the domain and then connecting the two ends to form a circle. We could also reverse that to be the next smaller number than negative 32768 is positive 32767.

Using a two-byte integer, the next number bigger than 32767 is negative 32768 (character acts the same way going from 255 to 0. The integer family has a circular wrap-around feature. Second, the integer data type is often used to control program flow by counting (counting loops). A dog, even with only 3 legs, is still one dog not three-fourths of a dog. First, some things in the real world are not fractional. It could be asked why not make all your numbers floating-point data types. There is nothing between 6 and 7 nor between ‘A’ and ‘B’. The integer family values jump from one value to another. Maybe we should say they act differently than the floating-point data types. There are times when character and integer data types are lumped together because they both act the same (often called the integer family). In particular, if the possibility has not been anticipated, overflow can compromise a program’s reliability and security. An overflow condition may give results leading to unintended behavior. The most common result of an overflow is that the least significant representable bits of the result are stored the result is said to wrap around the maximum (i.e. Integer overflow occurs when an arithmetic operation attempts to create a numeric value that is outside of the range that can be represented with a given number of bits – either larger than the maximum or lower than the minimum representable value.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
